

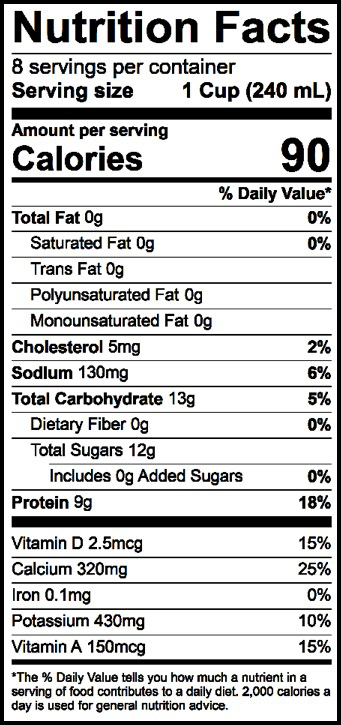
There was no marked change in the lactose content due to any of the three treatments and subsequent refiltering of the treated permeates. On refiltering the treated permeates approximately 42, approximately 50, and approximately 70% of the total calcium present could be recovered from 1) heat-treated, 2) pH-adjusted, and 3) pH-adjusted and heat-treated permeates, respectively. This is even higher than the calcium content of whole milk. It also contains minimal amounts of sodium, which be hard on kidneys if consumed in large quantities. In fact, skim milk is one of the richest food sources of calcium, providing around 325 mg per cup. Similarly, there are 4.7 grams of carbohydrates in standard half-and-half.
Calcium in skim milk full#
Regardless of whether it is skim milk or full cream milk, there are between 4.8 and 5 grams of carbohydrates per 100 grams of milk. The three treatments applied produced white precipitates and turned the clear permeates turbid. Coconut milk is an ideal for calcium absorption due to its high content in magnesium which helps improve bone strength, making it a better alternative than soy-based alternatives when it comes to calcium intake. The carbohydrate content in standard half-and-half is similar to most types of milk. About 76% of the total lactose and about 16% of the calcium present in skim milk permeated through the membrane during ultrafiltration. Skim milk, retentates, permeates, and the treated permeates were analyzed for total solids, ash, protein, or total nitrogen, calcium, and lactose content. The process was first developed at laboratory scale, and then its applicability was tested at the pilot scale. Of course, all milk is a good source of calcium, and so this isn’t a unique point, but skim milk does have the best protein density. Then, the calcium present in permeate was precipitated using one of three methods: 1) heat treatment, 2) pH adjustment, or 3) a combination of pH adjustment and heat treatment to permeate, then recovered by refiltering permeate. There are two main benefits of skim milk protein and calcium content. In this study, a process was developed in which first the lactose reduction in skim milk was achieved by ultrafiltration (4x volumetric concentration) using a 10-kDa membrane. Almond milk contains far fewer calories than cows milk. However, during ultrafiltration, valuable minerals, such as calcium in soluble form, are also lost into permeate. Ultrafiltration is a known process of removing lactose from these products. The physico-chemical and tribo-rheological characteristics of calcium-induced skim milk gels obtained by heating of milk dispersions prepared with different concentrations of skim milk powder (10, 20 and 30 w/w) and calcium chloride (30, 60 and 90 mmol kg 1) were studied. These nutrients are best obtained as part of a healthful dietary pattern, which can include calcium-fortified foods.Lactose is separated from milk or other fluid dairy products for a variety of reasons. And, although people tend to focus on calcium and vitamin D for bone health, many other nutrients, such as potassium, magnesium, zinc, vitamin C and vitamin K, also are important for bones. Calcium-fortified foods typically contain smaller amounts of calcium than dedicated supplements. “Calcium is better absorbed and utilized if consumed in smaller amounts spread out during the day. Including such foods is far better than having a calcium-deficient diet. The availability of healthful calcium-fortified foods, such as soy milk, tofu, whole-grain cereal and juice (in moderation) can be useful to these individuals. 207 Calcium-fortified cereals with milk (Total) 1 oz with 1/2 cup 350. Well, its a fact that the level of calcium in milk is high, and calcium helps you to maintain normal bones and teeth throughout life. For vegans and individuals who do not tolerate or care for dairy foods, which are the main sources of dietary calcium in the US, it can be challenging to meet the calcium requirement each day. NUTRITIONAL COMPOSITION OF SKIM MILK POWDER Nutrients Value Per 100 g of Powder Protein 34.037.0 Individual Amino Acids Tryptophan 0.51g Threonine 1.63 g Isoleucine,a 2.18 g Leucine,a 3.54 g Lysine 2.86 g Methionine 0.99 g Cystine 0.33 g Phenylanine 1.74 g Tyrosine 1.74 g Valine,a 2.42 g Arginine 1. How are calcium-fortified foods any better than calcium supplements?īess Dawson-Hughes, MD, director of Tufts’ HNRCA Bone Metabolism Laboratory, answers:Ī:“Food fortification is a long-standing and safe approach to boost intake of selected nutrients (for example, milk is fortified with vitamin D).

Q: We’re often told food sources of calcium are best, but calcium-fortified foods are often included in this advice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
